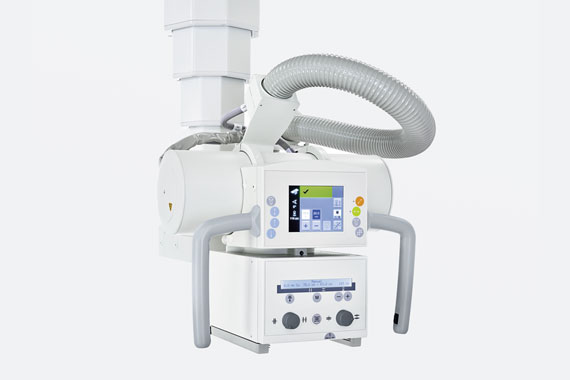
X-ray
In X-rays, similar to photography with flash light, a short X-ray flash is triggered by applying electricity, which exposes a sensitive film (detector) on the other side of the patient through the patient. The imaged organs cast a shadow on the detector during X-ray, thus important information about lung diseases and bone fractures can be found.
X-ray fluoroscopy
In this examination, similar to video filming, many sequential images are calculated from a series of X-ray flashes by very fast detectors. With the help of contrast medium, information about the gastrointestinal tract can be obtained with this X-ray examination.

- Elastography
- X-ray lumbar spine
- X-ray cervical spine with function
- Mammography
- Shoulder X-ray
- X-ray spine full
- Rib X-ray
- Esophageal X-ray
- Stomach x-ray
- Lung X-ray
- Lumbar spine with functional image
- Knee x-ray
- Orthodontics remote exposure
- Hip X-ray
- Hand X-ray
- Elbow X-ray
- Direct point of contact and assessment for unclear mammography findings (BIRADS 0).